Geofences
Geofences represent custom regions or places monitored in your project. Depending on your use case, a geofence might represent a retail store, a neighborhood, and so on.
Radar geofencing is more powerful than native iOS or Android geofencing, with cross-platform support for unlimited geofences, polygon geofences, isochrone (time-based) geofences, temporary geofences, and stop detection.

Geofences provides the following user context:
{ "geofences": [ { "tag": "store", "externalId": "123", "description": "Store #123", "metadata": { "parking": false } } ]}Geofences also provides the following events:
user.entered_geofenceuser.exited_geofenceuser.dwelled_in_geofence
You can receive events client-side via the SDK or server-side via event integrations, including webhooks.
You can create geofences via the dashboard, CSV import, the API, nightly sync, or integrations.
Alternatively, if you don't have your own custom place data, Radar can detect when a user visits a place even if you haven't set up a geofence for that place. Learn more about Places.
Quickstart#
First, sign up for Radar and get an API key.
Then, create geofences.
From there, integrate the SDK and call Radar.trackOnce() or Radar.startTracking(), depending on your use case. Radar will generate an entry event on the first location update inside of a geofence.
How it works#
Geofencing works in the foreground and in the background. All event generation happens server-side. This allows Radar geofencing to be more powerful than native iOS or Android geofencing, with cross-platform support for unlimited geofences, polygon geofences, isochrone (time-based) geofences, temporary geofences, and stop detection.
Radar generates a geofence entry event if a user enters a geofence (if stop detection is off) or stops in a geofence (if stop detection is on) with sufficient confidence, then a geofence exit event when the user leaves the geofence with sufficient confidence. A device must exit a geofence before a subsequent entry into that same geofence.
Create geofences#
You can create geofences via the dashboard, CSV import, the API, nightly sync, or integrations. You can create geofences in the Test environment for development and testing, and in the Live environment for production.
You specify the metadata for geofences when you create them, including the tag (a group for the geofence, e.g., store), external ID (an external ID for the geofence that maps to your internal database, e.g., 123), and description (a display name for the geofence, e.g., Store #123).
Geofences should be uniquely referenced by tag and external ID, assigned by you when a geofence is created. To disable or update metadata for a geofence, re-import the geofence with the same tag and external ID.
Dashboard#
To create a geofence via the dashboard, go to the Geofences page and click the Create button. Optionally search for an address or place, then enter a description, tag, external ID, and optional metadata. Choose circle to create a circle geofence, polygon to create a polygon geofence, or isochrone to create an isochrone (time-based) geofence. Click Create to create the geofence.
CSV import#
To create geofences via CSV import, go to the Geofences page and click the Import button. Then, select a CSV to upload.
The CSV may have the following columns:
description(string, required): A description for the geofence.type(string, required): The type of geofence geometry.polygon,circle, andisochroneare supported.tag(string, required): A group for the geofence.externalId(string, required): An external ID for the geofence that maps to your internal database.coordinates(array, required ifaddressandplaceIdare not included): An array or JSON string representing a center for typecircleor a destination for typeisochronein the format[longitude,latitude]. A two-dimensional array or JSON string representing a closed ring of between 4 and 2,000 coordinates in the format[[longitude0, latitude0],[longitude1,latitude1],[longitude2,latitude2],...,[longitude0,latitude0]]for typepolygon. Note that longitude comes before latitude, a GeoJSON convention.address(string, required ifcoordinatesandplaceIdare not included): An address to search for, and if found, will represent the center for typecircleorisochrone. Ifaddressandcoordinatesare both provided, they must be nearby, andcoordinateswill take precedent. Ignored for typepolygon.radius(number, required for typecircleandisochrone): The radius in meters for typecircle, a number between10and10000. The travel duration in minutes for typeisochrone. Ignored for typepolygon.mode(required for typeisochrone): the travel mode for typeisochrone.enabled(boolean, optional): Iftrue, the geofence will generate events. Iffalse, the geofence will not generate events. Defaults totrue.metadata(dictionary, optional): An optional set of custom key-value pairs for the geofence. A dictionary or JSON string with up to 16 keys and values of type string, boolean, or number. Cannot be used withmetadata.{key}columns.metadata.{key}(string, optional): Instead of convertingmetadatato stringified JSON, use columns of this format to add a key-value pairs tometadata. For example, the column headermetadata.pickup-modewith a value of"drive-thru"will resolve to{ pickup-mode: "drive-thru" }. Avoid using spaces and commas for keys. Cannot be used with themetadatacolumn.operatingHours(dictionary, optional): An optional set of key-value pairs restricting the operating hours of the geofence. Each key is a day of the week (e.g.,Sunday) or the three letter abbreviation of the day (e.g.,Sun), case insensitive. Each value is a list of pairs, where a pair indicates one opening and closing time for that day. For example, a restaurant only open for lunch and dinner on Sundays would be{ Sunday: [["11:00", "14:00"], ["19:00", "22:00"]] }. Accepted time formats includeh:mm aa(e.g.,12:45 AM) andHH:mm(e.g.,00:45). If neitheroperatingHoursnoroperatingHours.{day}is provided, the geofence will always be open. Cannot be used withoperatingHours.{day}columns.operatingHours.{day}(string, optional): Instead of convertingoperatingHoursto stringified JSON, use columns of this format to add a key-value pairs tooperatingHours. For example, the column headeroperatingHours.sunday(oroperatingHours.sun) with a value of"[["11:00", "14:00"], ["19:00", "22:00"]]"will resolve to{ Sunday: [["11:00", "14:00"], ["19:00", "22:00"]] }. If neitheroperatingHoursnoroperatingHours.{day}is provided, the geofence will always be open. Cannot be used with theoperatingHourscolumn.stopDetection(boolean, optional): The stop detection setting for the geofence. Overrides the project-level stop detection setting.disableAfter(datetime, optional): Use to create temporary geofences. If set, the geofence will be disabled after the specified datetime.disableAfteroperates independently ofoperatingHours. A date or valid ISO date string.deleteAfter(datetime, optional): Use to create temporary geofences. If set, the geofence will be deleted after the specified datetime. A date or valid ISO date string.userId(string, optional): An optional user restriction for the geofence. If set, the geofence will only generate events for the specified user. If not set, the geofence will generate events for all users.ip(string, optional): An optional IP address restriction for the geofence. A string of comma-separated IP address ranges, each of which could be a single IP (8.8.8.8), wildcard notation (8.8.8.*), or CIDR notation (8.8.8.8/24). If set, the geofence will only generate events for requests from the specified IP address. If not set, the geofence will generate events for all requests.dwellThreshold(number, optional): An optional field to trigger dwell events. If set anduser.dwelled_in_geofenceis enabled in settings, an event is triggered when a user dwells in the geofence longer than the threshold (in minutes). For example, a value of10would result in a dwell event on the next track call after a user has occupied a geofence for 10 minutes.placeId(string, required ifcoordinatesandaddressare not included): For place matching, an optional_idof the Radar place to match to the geofence. If a place was matched, the geometry of the place will override the geometry of the geofence.
If a geofence with the specified tag and external ID already exists, it will be updated. If not, it will be created.
For example, to import a circle geofence representing a store and a polygon geofence representing a neighborhood, you could use the following CSV:
description,tag,externalId,type,radius,mode,coordinates,address,enabled,metadata,stopDetection,disableAfter,deleteAfter,userId,operatingHours"Store #123",store,123,circle,50,,"[-73.975363,40.783826]",,true,"{""parking"":false}",,,,,"SoHo",neighborhood,soho,polygon,,,"[[-73.996973,40.725660],[-73.998282,40.726294],[-74.001072,40.727660],[-74.002853,40.728603],[-74.003282,40.727936],[-74.003840,40.726310],[-74.004226,40.725351],[-74.004998,40.723530],[-74.005191,40.722993],[-74.005556,40.722115],[-74.004462,40.721334],[-74.001908,40.719496],[-73.999827,40.718016],[-73.997467,40.720863],[-73.997016,40.722212],[-73.996501,40.723497],[-73.995750,40.724278],[-73.995128,40.725107],[-73.996973,40.725660]]",,true,,,,,,"15 minutes driving to Disney World","car-15",disney,isochrone,15,car,"[-81.563874,28.385233]",,true,"{""type"":""resort""}",,,,,"Madison Square Garden from address",stadium,msg,circle,200,,,"4 Pennsylvania Plaza, New York, NY 10001",true,,,,,,"Disable in 2028 and delete in 2029",new-years,2027,circle,50,,"[-73.9877313,40.7579787]",,true,,,"2028-01-01T00:01:00-05:00","Jan 1, 2029",,"Delivery #123 for user #456",delivery,123,circle,50,,"[-73.9934387,40.7505045]",,true,,,,,456,"Restaurant #789 open for Sunday breakfast and dinner",restaurant,789,circle,50,,"[-73.9934387,40.7505045]",,true,,,,,,"{""Sun"":[[""09:00"",""14:00""], [""17:00"",""22:00""]]}"Again, note that longitude comes before latitude, a GeoJSON convention.
You can find a history of past imports on the Geofences import history page.
API#
You can also create geofences programmatically via the API. You can create a geofence via POST /api/v1/geofences, or upsert a geofence based on tag and external ID via PUT /api/v1/geofences/:tag/:externalId.
For example, to upsert a geofence representing a store via the API:
curl https://api.radar.io/v1/geofences/store/123 \ -H "Authorization: prj_live_sk_..." \ -X PUT \ -d "description=Store #123" \ -d "type=circle" \ -d "coordinates=[-73.975363,40.783826]" \ -d "radius=100"Again, note that longitude comes before latitude, a GeoJSON convention.
Geofence sync#
Finally, you can sync geofences nightly from a CSV.
On the Radar Integrations page under Geofence Sync, set Enabled to Yes. Enter a Notification Email to receive success and failure confirmation emails. Then, choose a Protocol:
- Choose HTTP for geofence CSVs at public HTTP or HTTPS URLs. Enter the URLs of the geofence CSVs.
- Or, choose AWS S3 for geofence CSVs in a private S3 bucket. Enter an S3 bucket region, S3 bucket name, and the S3 object keys of the geofence CSVs. Finally, enter the AWS access key ID and secret access key of an IAM user with
GetObjectpermissions for the specified S3 bucket and objects.
Note that you can set separate CSVs for the Test and Live environments.
The geofence sync CSV format is the same as the geofence import CSV format.
When you click Save and Sync, Radar will attempt a one-time sync and send an email on success or failure. Radar will then attempt syncs nightly.
Confidence and accuracy#
All geofence events have confidence levels. Confidence levels range from 1 (low) to 3 (high). Confidence is a function of the accuracy of the location reported by the device and the geometry of the geofence.
Confidence will be high when the user, taking into account the accuracy of the location reported by the device, is completely inside the geofence. Confidence will be medium when the user is mostly inside the geofence. Confidence will be low when the user is only partially inside the geofence.
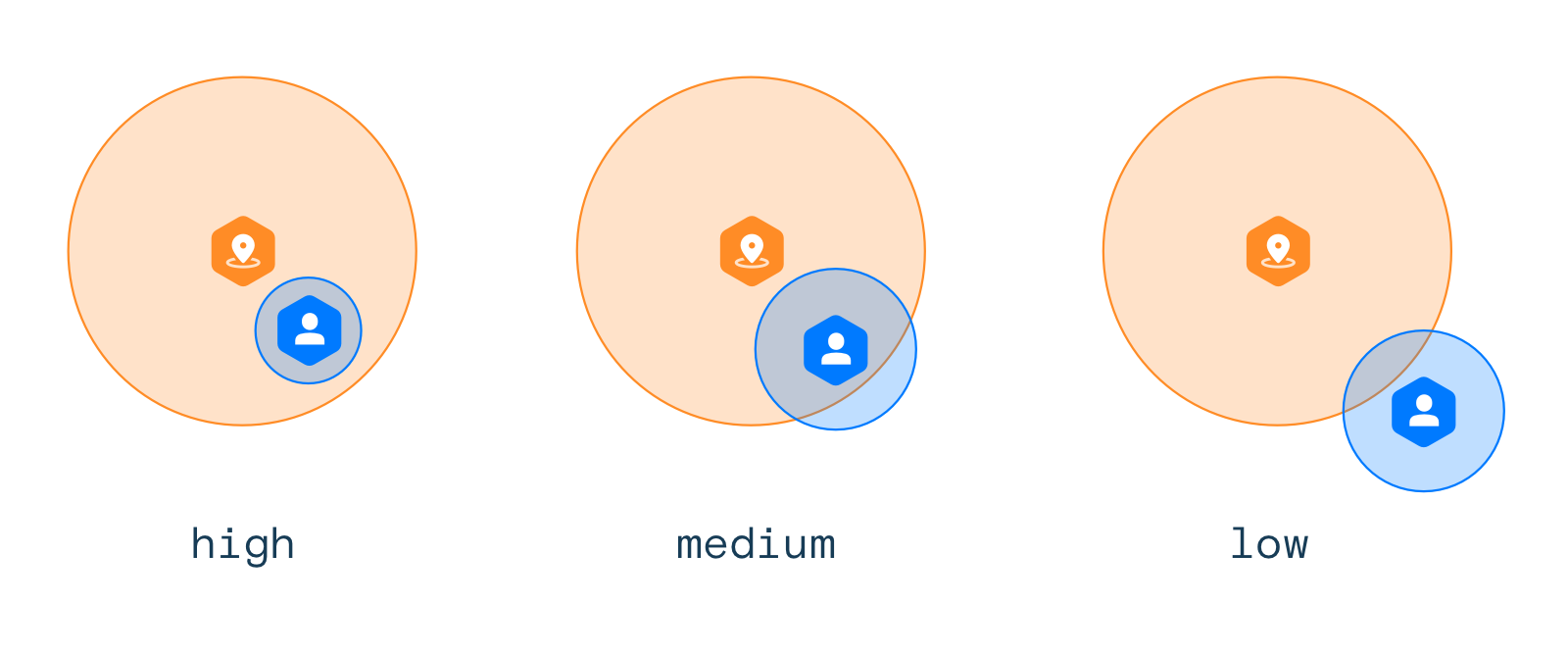
The smaller the geofence and the less accurate the location reported by the device, the lower the confidence level. As a result, you may decide to ignore some events based on confidence levels.
Stop detection#
When Geofence stop detection is on, Radar can understand the difference between a user walking or driving through a geofence and stopping in a geofence, and will only generate a geofence entry event when a user stops in a geofence (i.e., when stopped is true based on tracking options or when foreground is true).
You can enable this setting at a project level on the Settings page, or at a geofence level when you create geofences.
Buffer entries and exits#
Use Buffer entries to more aggressively enter geofences and reduce the likelihood of missed entry events. When Buffer Entries is off, Radar will only generate an entry event if the location reported by the device is inside the geofence boundary. However, when Buffer Entries is on, Radar will generate an entry event if the device is within X meters of the geofence, where X is the accuracy reported by the device. For example, if the device reports a location accurate to within 50 meters, Radar will generate an entry event if the location is within 50 meters of the geofence boundary.
Use Buffer exits to more conservatively exit geofences and reduce the jumpiness of exit events. When Buffer Exits is off, Radar will generate an exit event if the location reported by the device is outside the geofence boundary. However, when Buffer Exits is on, Radar will only generate an exit event if the device is more than X meters outside of the geofence, where X is the accuracy reported by the device. For example, if the device reports a location accurate to within 50 meters, Radar will only generate an entry event if the location is more than 50 meters outside of the geofence boundary.
You can enable these settings at a project level at a project level on the Settings page.
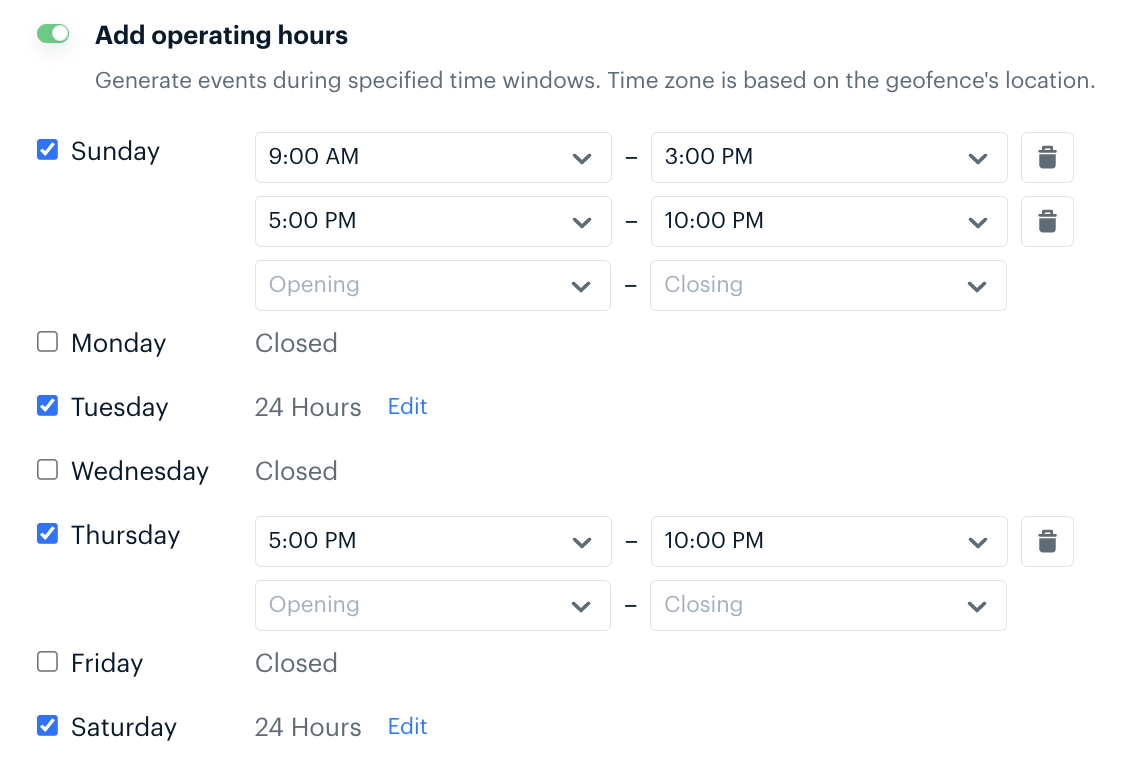
Operating hours#
When Operating Hours are set on a geofence, Radar will indicate whether a user entered, exited, or dwelled in the geofence during its operating hours. Radar will add a boolean flag currentlyOperating to all geofence event payloads.
Radar can also restrict geofence events from being generated outside of operating hours. Restrict event generation to only operating hours at the project level on the Settings page.
Operating hours can be set on individual geofences via CSV import, the API, or in the Advanced section of the geofence create and edit pages.
Dwell events#
If user.dwelled_in_geofence is enabled, Radar can trigger dwell events after a device remains inside of a geofence boundary for more than a specific threshold. Radar will generate a dwell event after the first location reported by the device beyond the specified threshold.
You can enable this event at the project level on the Settings page.